
@ AAAI 2025
Fourth Workshop on Multimodal Fact Checking and Hate Speech
Detection
February, 2025
CT2: AI-Generated Text Detection
Important News Datasets Released:
CT2 - AI Generated Text Detection
- Deadline Extended to 14th December 2024
- Check the leaderboard: Leaderboard
- Fill the form to submit your scores to the leaderboard: Leaderboard Form
- Updated Test Dataset Shared on 2nd December. Kindly fill the form to get access to the drive link and dataset.
- Colab: https://codalab.lisn.upsaclay.fr/competitions/20330
- Form: https://forms.gle/bQcnFWv1dUoeMwZbA
Dataset:
To better understand which types of LLM-generated content are easier or harder to detect, we will include the following families of LLMs:
- Encoder models: (e.g., BERT, DeBERTa)
- Open-Source: (e.g., Llama 3.1, Yi-2)
- Closed-Source: (e.g., Claude 3.5 Sonnet, GPT 4.0/mini)
- SLMs: (e.g., Phi-3.5)
- Mixture of Experts (MoEs) (e.g., Mixtral)
- State Space Models (SSM) (e.g., Falcon-Mamba)
We will be releasing 50K data samples for this task. The data will be structured such that each prompt will have a human-written story and corresponding parallel generations from all the included LLMs. A snapshot of the data can be viewed here.
Tasks:
CT2 for text will consist of two sub-tasks:
- Task A: This is a binary classification task where the goal is to determine whether each given text document was generated by AI or created by a human.
- Task B: Building on Task A, this task requires participants to identify which specific LLM generated a given piece of AI-generated text. For this task, participants will know that the text is AI-generated and must predict whether it was produced by models such as GPT 4.0, DeBERTa, FalconMamba, Phi-3.5, or others.
Baseline:
Several systems for detecting AI-generated text, such as GPT-2 Output Detector, GLTR, and GPTZero, have recently emerged. However, these proprietary tools do not disclose their detection methods. In academic research, various techniques have been proposed to identify AI-generated text, including:
- Perplexity estimation
- Burstiness estimation
- Negative log-likelihood curvature
- Stylometric variation
- Intrinsic property based approaches
- Classifier-based approaches (RADAR, Conda)
A new interesting technique proposed at ICML 2024 finds that LLMs are more inclined to modify human-written text than AI-generated text when tasked with rewriting. This approach, named the geneRative AI Detection viA Rewriting method (Raidar), will be used as the baseline for both Tasks A and B.
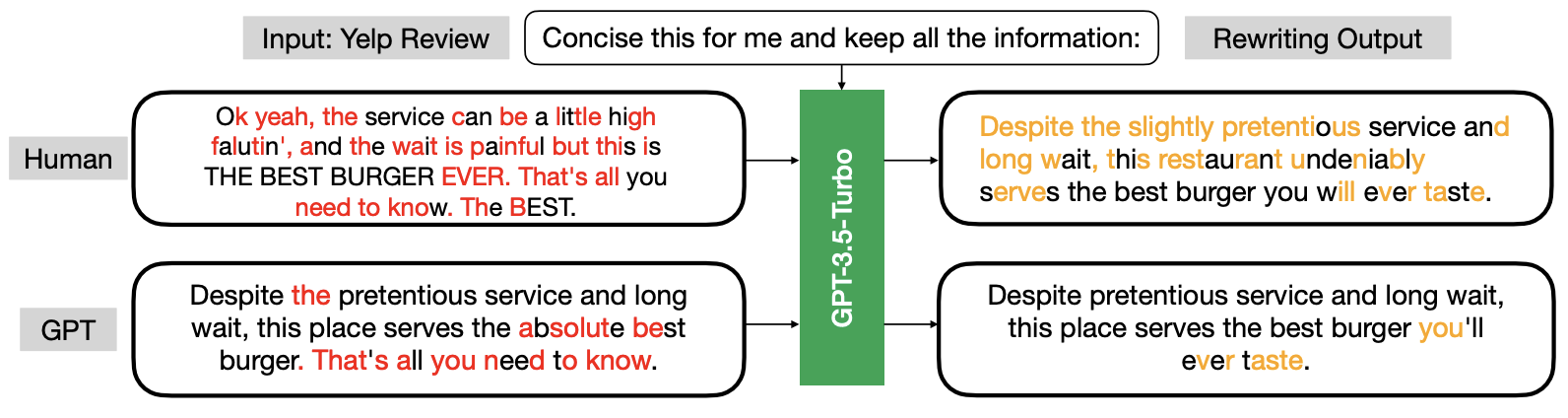
The authors highlight character deletions in red and character insertions in orange. Their findings indicate that human-generated text generally prompts more modifications compared to machine-generated text when rewritten.
IMPORTANT DATES
- 31 October 2024: Release of the training set.
- 10 November 2024: Release of the test set.
- 2 December 2024: Release of the Updated test set.
- 30 November 14 December 2024: Deadline for submitting the final results.
- 20 December 2024: Announcement of the results.
- 16 January 2025: System paper submission deadline (All teams are invited to submit a paper).
- 20 January 2025: Notification of system papers.
- 25 January 2025: Camera-ready submission.
Leaderboard
| S.No | Name | Team Name | Score for Task-A ▲▼ | Score for Task-B ▲▼ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Avinash Trivedi | Sarang | 1 | 0.9531 |
| 2 | Duong Anh Kiet | dakiet | 0.9999 | 0.9082 |
| 3 | Vijayasaradhi Indurthi | tesla | 0.9962 | 0.9218 |
| 4 | Shrikant Malviya | SKDU | 0.9945 | 0.7615 |
| 5 | Harika Abburi | Drocks | 0.9941 | 0.627 |
| 6 | Manoj Saravanan | Llama_Mamba | 0.988 | 0.4551 |
| 7 | Chinnappa Guggilla | AI_Blues | 0.9547 | 0.4698 |
| 8 | Xinlong Zhang | NLP_great | 0.9157 | 0.1874 |
| 9 | Shifali Agrahari | Osint | 0.8982 | 0.3072 |
| 10 | Xiaoyu | Xiaoyu | 0.803 | 0.5696 |
| 11 | Rohan R | Rohan | 0.7546 | 0.4053 |
Leaderboard-Subtask
Leaderboard for Task-A Scores
| S.No | Name | Team Name | Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Avinash Trivedi | Sarang | 1 |
| 2 | Duong Anh Kiet | dakiet | 0.9999 |
| 3 | Vijayasaradhi Indurthi | tesla | 0.9962 |
| 4 | Shrikant Malviya | SKDU | 0.9945 |
| 5 | Harika Abburi | Drocks | 0.9941 |
| 6 | Manoj Saravanan | Llama_Mamba | 0.988 |
| 7 | Chinnappa Guggilla | AI_Blues | 0.9547 |
| 8 | Xinlong Zhang | NLP_great | 0.9157 |
| 9 | Shifali Agrahari | Osint | 0.8982 |
| 10 | Xiaoyu | Xiaoyu | 0.803 |
| 11 | Rohan R | Rohan | 0.7546 |
Leaderboard for Task-B Scores
| S.No | Name | Team Name | Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Avinash Trivedi | Sarang | 0.9531 |
| 2 | Vijayasaradhi Indurthi | tesla | 0.9218 |
| 3 | Duong Anh Kiet | dakiet | 0.9082 |
| 4 | Shrikant Malviya | SKDU | 0.7615 |
| 5 | Harika Abburi | Drocks | 0.627 |
| 6 | Xiaoyu | Xiaoyu | 0.5696 |
| 7 | Chinnappa Guggilla | AI_Blues | 0.4698 |
| 8 | Manoj Saravanan | Llama_Mamba | 0.4551 |
| 9 | Rohan R | Rohan | 0.4053 |
| 10 | Shifali Agrahari | Osint | 0.3072 |
| 11 | Xinlong Zhang | NLP_great | 0.1874 |